Autism PDA Explained: The Core Characteristics of Pathological Demand Avoidance

Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA) is a term used to describe a profile of autism that is characterized by an intense, pervasive drive for autonomy and a heightened sensitivity to demands that threaten that autonomy. For individuals with PDA, simple, everyday demands like putting on shoes or eating breakfast can trigger big emotional reactions that can be difficult for caregivers and loved ones to understand. In this post, we’ll explore what PDA is, and its core characteristics. So whether you’re a caregiver, parent, or just someone interested in learning more about autism PDA, this infographic is for you.
What is Pathological Demand Avoidance?
Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA), also known as Pervasive Drive for Autonomy, is a term used to describe a profile of autism. People with PDA can experience a fight, flight or freeze response when faced with demands that threaten their autonomy, which can trigger intense emotional reactions. Understanding the core characteristics of PDA can help caregivers and healthcare professionals respond with more empathy and attunement, which is crucial for effectively supporting individuals with PDA.
I’m excited to announce that the Master Class on PDA is now live and on sale! You can purchase it for $29! (Use code PDA10) for a $10.00 coupon code.
What is PDA?
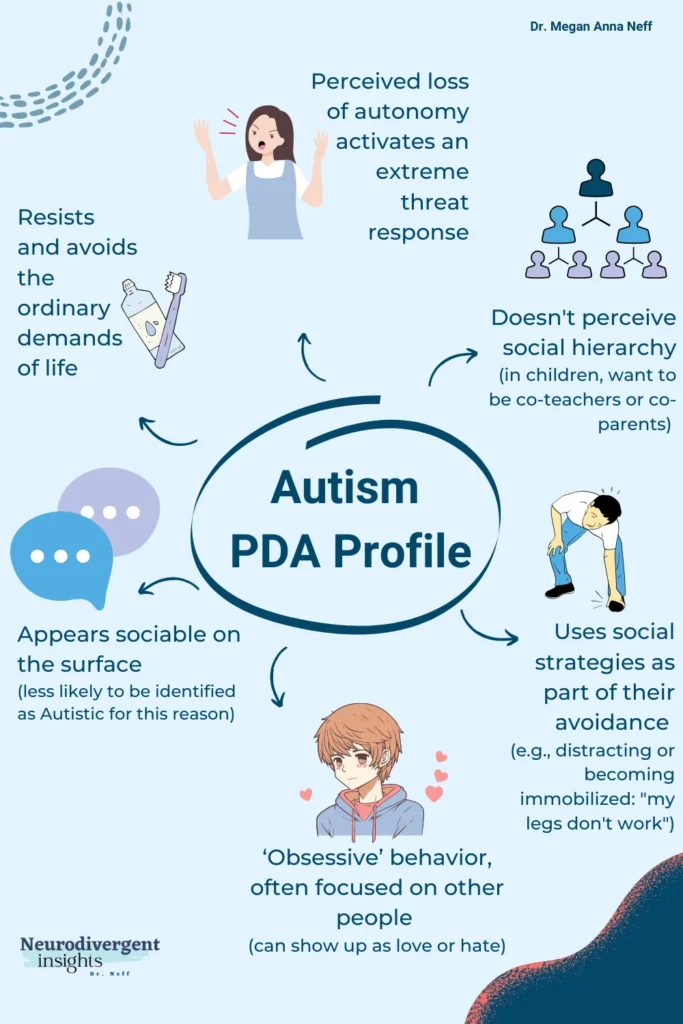
PDA, short for Pathological Demand Avoidance (or Pervasive Drive for Autonomy), is a concept predominantly acknowledged in the UK and not yet formally classified in the US. As a subtype of autism, it exhibits distinct characteristics characterized by a strong inclination to resist and avoid demands, even if the individual desires to fulfill them. The primary function of demand avoidance in PDA is to safeguard a person’s autonomy. Let’s explore the six core characteristics often associated with PDA:
The core characteristics of PDA include:
The following core characteristics commonly observed in PDA make it more difficult to observe autism:
1. Resistance and avoidance of everyday demands, including those that are perceived as trivial or routine
2. An overwhelming need to be in control and avoid being controlled by others.
3. Uses Social Strategies as part of their avoidance
4. Surface social communication abilities, despite difficulties with social interaction and understanding
5. ‘Obsessive’ behavior, often focused on other people or can be focused on performance demands (due to acute anxiety)
6. Appears comfortable in role play and pretend, sometimes to an extreme extent
Resists and avoids the ordinary demands of life
The most widely discussed characteristic of PDA is demand avoidance, which means that individuals with PDA resist and avoid the ordinary demands of life to an extreme extent, including things they enjoy. However, there are other traits that cluster with the PDA profile, which can lead to confusion for parents and healthcare professionals.
An overwhelming need to be in control
The loss of autonomy is perceived as a threat that activates the fight-flight or freeze response. This results in increased anxiety, sometimes to the point of panic, particularly when they feel they are not in control or feel exposed in some way. If the child responds with a fight or flight response, this can lead to emotional outbursts that may cause a child to be wrongly diagnosed with Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) or other behavioral disorders.
Uses Social Strategies as part of their avoidance
Another characteristic that can make PDA challenging to identify is the use of social strategies as part of avoidance. PDAers may be very good at ‘masking’ difficulties with certain people or in certain situations and may present differently in different settings depending on their anxiety levels.
For instance, they may employ various tactics such as distracting, excuse-making, outright refusal, ]or engaging in role-playing to avoid demands. At other times, their bodies may become immobilized in the face of the demand, and they will state, “my legs don’t work” (note their bodies may truly be immobilized in these moments).
Appears sociable on the surface
Another characteristic is that PDAers appear sociable on the surface, and difficulties in social communication and understanding may be less obvious than in typical autism presentations. They may have good verbal fluency, which can disguise difficulties in understanding and processing allistic communication. Additionally, they are likely to struggle to understand or perceive social hierarchy and may want to be co-teachers, and co-parents and have the same social role as authority figures.
Experiences excessive mood swings and impulsivity
Individuals with PDA experience excessive mood swings and impulsivity and have extreme emotional reactions. Some individuals become quiet/withdrawn, while others become externalizers and display obvious emotional reactions. Their flight, fight, freeze, or fawn responses are outward representations of the brain and body’s instinctual response to physiological stress.
‘Obsessive’ behavior, often focused on other people
PDAers often exhibit ‘obsessive’ behavior that is often focused on other people, and they may have developed passionate interests and be able to be hyper-focused. This ‘obsessive’ behavior is often social in nature and may show up as extreme love or hate.
Obsessive behavior may also present as obsessive behavior with ‘social’ or ‘performance-based’ demands due to acute anxiety and/or because a demand conflicts with an intense need to be seen as independent and undependable.
Appears comfortable in role play and pretend, sometimes to an extreme extent
They appear comfortable in role play and pretend, and their play can be quite imaginative. When they involve others in their role-play, they are usually controlling the themes, roles, and dialogue.
PDA, Misdiagnosis, and Misunderstandings
Unfortunately, people with PDA often face misunderstanding and misdiagnosis. PDA can mask or influence the presentation of Autistic traits, leading to confusion and difficulty in identifying autism. Additionally, PDA can often go unrecognized and is frequently misdiagnosed with behavioral disorders (such as ODD and conduct disorder), leading to a blame game that puts the burden on the individual and their parents for their explosive meltdowns and responses to autonomy threats. This can leave parents feeling helpless and confused after trying a variety of therapies, medications, and parenting tactics.
It is crucial to recognize and understand the characteristics of PDA in order to support individuals with PDA. Recognizing and understanding the characteristics of PDA is crucial for effectively supporting PDAers.
The neurodivergent nervous system tends to be more rigid, meaning it more easily flips into a stressed state, making simple, everyday demands like “put on your shoes” challenging for people with PDA. Therefore, low-demand parenting approaches are often recommended to support individuals with PDA, focusing on reducing demands and offering choices that promote autonomy (You can read more about low-demand parenting in this blog post).
By understanding PDA, we can provide better support and accommodations for neurodivergent individuals who experience PDA. If you suspect that you or your child has PDA, it is important to seek professional help and support to develop an attuned plan that addresses the unique needs of you and your family.
Clinical Training for PDA
Unfortunately, because PDA is still not widely recognized, there are few formal training programs for learning about PDA (what it is, how to diagnose it, and how to treat it). That’s why I am so excited to let you know I’ve partnered with Dr. Donna Henderson to create a Master Class on PDA. Here she walks through the six core traits of PDA, busts common myths about PDA, describes how it differs from oppositional defiant disorder, and how to support PDAers. You can grab lifetime access to this 90-minute Master Class here. (Use code PDA10 to get $10.00 off).

Parenting Resources for PDA
✦ Amanda Diekman (Author of Low Demand Parenting and PDAer) is hosting a 2024 Low Demand Parenting summit with a great line up of speakers! It’s free if you attend live, or you can access all access pass to watch at a leisurely pace.
✦ The PDA Society also offers a variety of free resources and guides, including a comprehensive booklet on what PDA is, as well as their PANDA approach to implementing low-arousal strategies in parenting. Their guide for parents of PDAers is particularly helpful.
✦Another excellent resource is Amanda Diekman’s book, Low-Demand Parenting: Dropping Demands, Restoring Calm, and Finding Connection with Your Uniquely Wired Child. This book offers practical advice and guidance for implementing low-demand parenting strategies in your home.
Megan Anna Neff

Welcome! I’m Dr. Neff. I am a late-in-life diagnosed Autistic-ADHD Psychologist. Welcome to my little corner of the internet where I love talking about all things mental health, neurodiversity and wellness.







