Have you ever found yourself in a situation where it feels like your nervous system is on high alert, amplifying every sensory input around you? In those moments, even the most insignificant touch or sound can push you to the edge of overwhelm. To outsiders, it may appear as a simple emotional outburst or tantrum, but beneath the surface lies something deeper: your sensory system in a state of overload.
As someone who has personally weathered the storm of sensory dysregulation and overload, I intimately understand the profound impact it can have on our emotions, ability to focus, and to self-regulate. It can feel disorienting, overwhelming, and isolating. Until I began examining these experiences through the lens of sensory regulation, understanding them remained a mystery. However, through my neurodivergent journey, I’ve come to recognize that sensory regulation serves as the bedrock for various other self-regulation systems, including emotions, executive functioning, and behavior.
Once I understood the foundational role of sensory regulation in my life, I started to prioritize my sensory needs. In this blog post, we lay the groundwork for this series by exploring the following key aspects:
Defining sensory regulation and its impact on self-regulation.
Unveiling the intricacies of sensory dysregulation.
Understanding the importance of sensory regulation and strategies for improvement.
Before we delve into these complexities, let’s establish clear definitions of sensory regulation and sensory dysregulation to ensure we’re starting on the same page.
What is Sensory Regulation?
Sensory regulation is a crucial process through which our nervous system integrates and adjusts sensory input, enabling us to maintain balance and optimal levels of arousal (energy). Essentially, sensory regulation involves our ability to respond to various sensory stimuli in our environment. When our sensory system is regulated, we can process and integrate sensory input in a way that allows us to navigate the world smoothly.
What Does Sensory Regulation Mean?
Sensory regulation involves integrating and adjusting sensory input and managing arousal levels, attention, and emotional responses. Sensory regulation significantly influences our ability to self-regulate and adapt to our environment. Whether it’s feeling the comforting warmth of a blanket or engaging with the sounds around us, sensory regulation enables us to filter, interpret, and adapt to our surroundings. By achieving sensory regulation, we lay the foundation for overall well-being and self-regulation.
When our sensory regulation is effectively maintained, our internal arousal aligns harmoniously with the energy of the environment. When we’re dysregulated, our internal arousal can become misaligned or disconnected from the energy of the environment, leading to challenges in processing sensory information and leading to a disequilibrium between our inner state and our environment.
What Does Sensory Regulation Look Like?
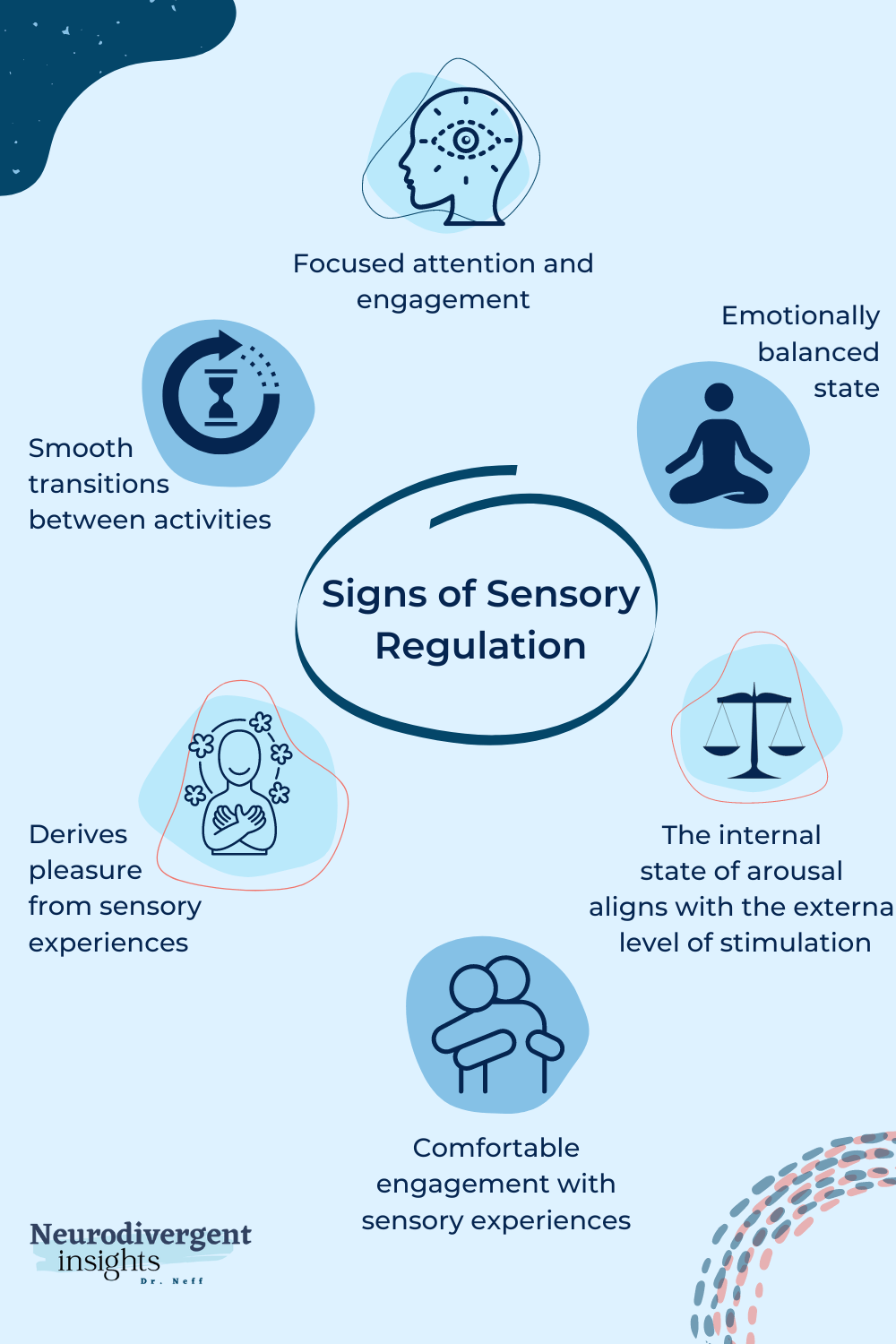 When we are sensory regulated we are able to move through our environment with ease. Things like transitioning from tasks, interacting with other people, taking in sensory information all run much more smoothly when we’re sensory-regulated. Here are some concrete examples of what sensory regulation can look like:
When we are sensory regulated we are able to move through our environment with ease. Things like transitioning from tasks, interacting with other people, taking in sensory information all run much more smoothly when we’re sensory-regulated. Here are some concrete examples of what sensory regulation can look like:
Focused attention and engagement: When we are sensory-regulated, we can more easily maintain focused attention on tasks or conversations without being easily distracted by sensory stimuli in our environment. We can have sustained engagement and more effectively filter out irrelevant sensory information.
Optimal response to sensory input: When sensory-regulated people demonstrate proportional reactions to sensory stimuli, maintaining a balanced response without excessive sensitivity or underreactivity. For instance, the ability to stay calm in the face of sudden noise or to be able to tolerate various textures without distress.
Smooth transitions between activities: People who are sensory regulated can transition smoothly between different sensory environments or activities without becoming overwhelmed or disoriented. They adapt well to changes in sensory input and adjust their responses accordingly.
Comfortable engagement with sensory experiences: When sensory regulated, we may seek out or enjoy sensory experiences that are aligned with our preferences. For instance, we might pursue a hug or engage in activities like swinging, rocking, or touching different textures to fulfill our sensory needs in a comfortable manner.
Emotionally balanced state: Sensory regulation often contributes to a stable emotional state. When someone is sensory regulated their emotions are more balanced, and they can effectively manage emotional responses to sensory input without becoming agitated or withdrawn.
Derives enjoyment from sensory experiences: When a person is sensory regulated, they can more easily experience pleasure and satisfaction in engaging with various sensory experiences. They may seek out activities or environments that provide sensory input aligned with their preferences, such as enjoying the taste of certain foods or finding delight in the sights and sounds of their surroundings.
What is Sensory Dysregulation
Sensory dysregulation occurs when our sensory processing system struggles to manage and respond to sensory stimuli effectively. It can result in difficulties in maintaining a proportional level of arousal and coping with sensory input. People with sensory dysregulation may experience heightened sensitivity or reduced sensitivity to sensory input. This can lead to being easily overwhelmed by certain:
sounds
textures
environments
or having trouble staying focused in visually stimulating situations
Sensory dysregulation significantly impacts our daily functioning, emotions, and overall well-being. Understanding sensory dysregulation is essential for developing strategies to support us in navigating and coping with sensory challenges.
Neurodivergent people are particularly prone to sensory dysregulation, given that our brains often process sensory input differently from neurotypical brains. By recognizing and addressing our specific sensory needs, we can create an environment that promotes our sensory regulation and well-being.
ADHD Sensory Overload
ADHD sensory overload is a common challenge experienced by ADHDers. Whether it’s an excess of sounds that we struggle to filter out, cognitive overload from receiving too much information at once, visual chaos, or other sensory triggers, our ADHD brains have a harder time managing and processing these inputs. As a result, we are more prone to sensory overload, which can lead to emotional meltdowns and difficulty maintaining focus. Recognizing the impact of sensory overload on our experiences is essential in developing effective strategies to manage and cope with its effects.
Autism and Sensory Overload
Sensory overload is also common among Autistic people. Sensory overload is frequently experienced by Autistic people. It often leads to overwhelming responses to sensory stimuli that we encounter. Our Autistic brains often have difficulty processing and regulating sensory input, which contributes to the heightened sensitivity and reactivity to sensory input. The challenges in sensory regulation can manifest in various ways, such as becoming overwhelmed by certain sounds, textures, or visual stimuli. Understanding the impact of sensory overload on our experiences is crucial in developing strategies to navigate and cope with the overwhelming sensory world we inhabit.

Sensory Dysregulation and Self-Regulation
The impact of sensory overload on our ability to regulate emotions, attention, and actions cannot be understated. It poses a significant challenge to our self-regulation skills, making it more difficult to navigate daily life.
Sensory regulation serves as a fundamental building block for self-regulation. Therefore, when we experience sensory dysregulation or overload, it inevitably affects our ability to effectively regulate other aspects of our lives. In the next section, we will delve into the intricate relationship between self-regulation and sensory regulation, shedding light on how these two systems are interconnected.
Self-Regulation and Sensory Regulation
 Sensory regulation acts as a catalyst for effective self-regulation. Sensory regulation forms the bedrock of self-regulation, influencing our emotions, behavior, attention, and even our relationships. By understanding the intricacies of sensory regulation, we can learn how to better care for ourselves in the midst of a sensory-rich world.
Sensory regulation acts as a catalyst for effective self-regulation. Sensory regulation forms the bedrock of self-regulation, influencing our emotions, behavior, attention, and even our relationships. By understanding the intricacies of sensory regulation, we can learn how to better care for ourselves in the midst of a sensory-rich world.
What is Self-Regulation?
Self-regulation refers to our ability to manage and control our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors in response to different situations and demands. It is an essential skill that allows us to:
- navigate challenges
- make sound decisions
- manage our emotions
- maintain a sense of balance and well-being.
Self-regulation involves monitoring and adjusting our internal states, such as our attention, impulses, and emotional reactions, to align with our goals and values.
At its core, self-regulation involves a relational dance between our thoughts, emotions, and actions. It is about understanding and recognizing our own feelings and needs, while also considering the impact of our behavior on others and the environment. Through self-regulation, we develop the capacity to modulate our responses and adapt to various circumstances.
Self-regulation encompasses several key components, including:
Self-awareness
Self-control
Self-monitoring
Self-awareness involves recognizing and understanding our emotions, thoughts, and physical sensations. Self-control is the ability to manage impulses and regulate our behavior, even in challenging situations. Self-monitoring entails keeping track of our own progress, reflecting on our actions, and making adjustments as needed.
By honing our self-regulation skills, we become better equipped to handle stress, regulate our emotions, and maintain focus amidst distractions. It empowers us to make choices that align with our values and long-term goals, rather than succumbing to immediate gratification. Furthermore, self-regulation helps foster resilience and adaptability, enabling us to navigate life’s ups and downs with greater ease.
How are Self-Regulation and Sensory Regulation Related?
As we’ve explored thus far, sensory overload can significantly impact our ability to regulate emotions, attention, and actions, making self-regulation a more challenging task. Sensory regulation is a fundamental foundation for self-regulation, influencing various aspects of our lives, including our emotions, behavior, attention, and relationships. It becomes evident that when we experience sensory dysregulation or overload has a ripple effect, impeding our ability to effectively regulate other aspects of our lives.
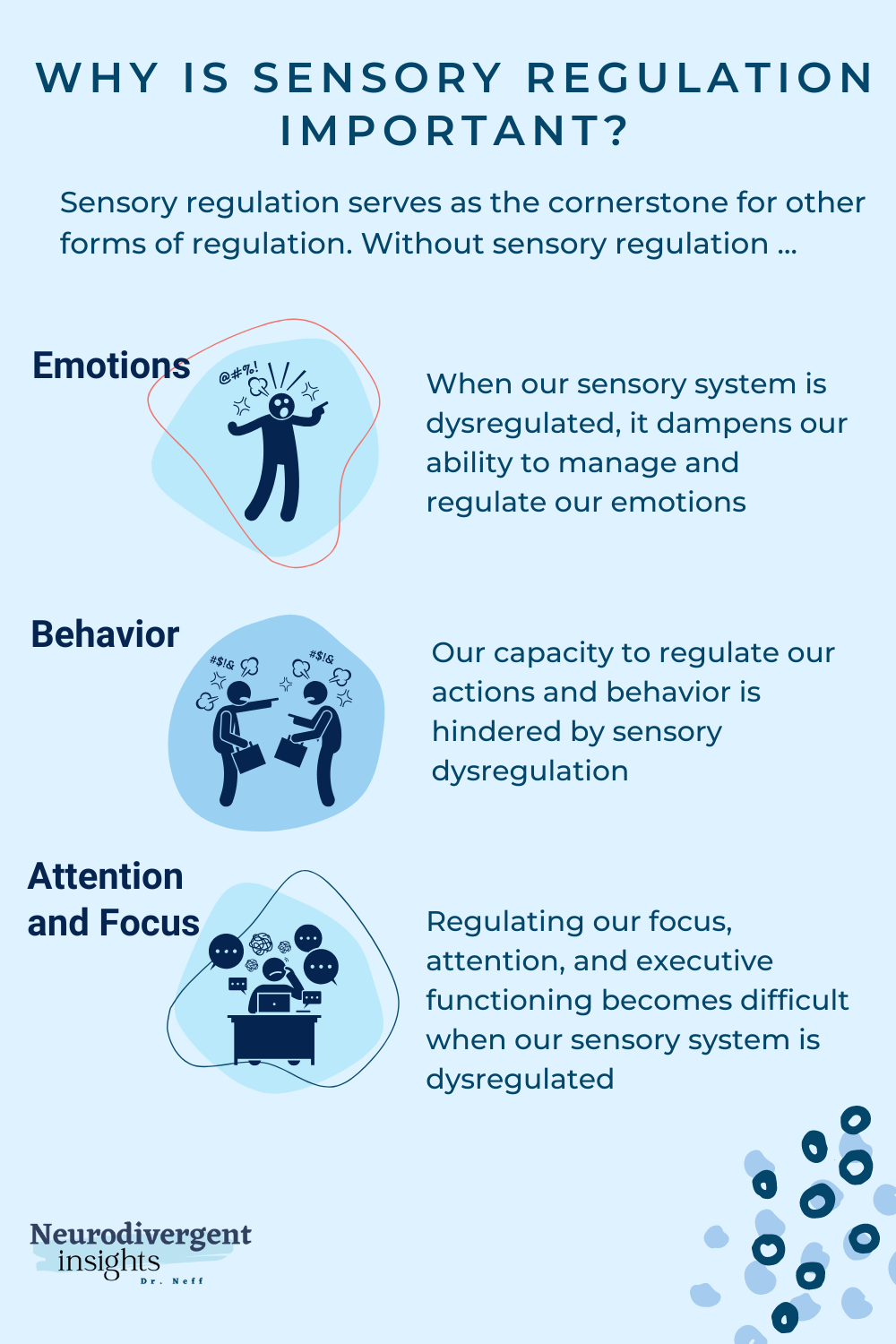 Sensory regulation serves as the cornerstone for other forms of regulation:
Sensory regulation serves as the cornerstone for other forms of regulation:
- When our sensory system is dysregulated, it hampers our ability to effectively manage and regulate our emotions.
- Regulating our focus, attention, and executive functioning becomes difficult when our sensory system is dysregulated.
- Our capacity to regulate our actions and behavior is hindered by sensory dysregulation.
When our sensory system is dysregulated or overloaded, it becomes a formidable challenge to effectively regulate our emotions, behavior, attention, and even our relationships. Understanding this intricate relationship is crucial in developing strategies to navigate and mitigate the impact of sensory overload on our daily lives.
Improved sensory regulation supports overall self-regulation by creating a balanced and harmonious sensory environment. And in return, improved self-regulation helps us to manage sensory overload more effectively! Nurturing both self-regulation and sensory regulation allows us to thrive in a world filled with diverse sensory experiences.
In essence, sensory regulation serves as the essential building block upon which the regulation of other aspects of our functioning relies. By establishing a solid foundation of sensory regulation, we pave the way for improved emotional regulation, enhanced cognitive regulation, and better control over our actions and behavior.
Sensory Regulation and Emotion Regulation
Sensory overload can have a significant impact on our emotional well-being. For those of us who have experienced sensory overload, we understand firsthand how it can disrupt our emotional well-being and interfere with our daily lives. The overwhelming influx of sensory stimuli can easily trigger heightened emotional responses, leading to frustration, anxiety, or even meltdowns. It becomes a constant battle to find balance and regain control in the face of overwhelming sensory input.
What is Emotion Regulation?
Emotion regulation refers to the ability to understand, manage, and adaptively respond to our emotions. It involves a set of skills and strategies that allow us to recognize and effectively navigate our emotional world.
Emotion regulation encompasses various processes, such as identifying and labeling emotions, understanding their causes and consequences, and implementing techniques to modulate their intensity and duration.
How is Emotion Regulation connected to Sensory regulation?
Sensory regulation plays a crucial role in emotion regulation by providing the foundation for managing emotional experiences. When sensory input is well-regulated, it can contribute to a more stable emotional state, allowing for better emotional regulation. On the other hand, challenges with sensory regulation, such as sensory overload, can disrupt emotion regulation and lead to difficulties in effectively managing and modulating emotions. Recognizing and addressing sensory regulation needs can create a more conducive environment for successful emotion regulation and resilience.
Sensory Regulation and Behavior Regulation
Sensory dysregulation can significantly influence our behavioral regulation. When faced with sensory overload, our attention and focus, and emotions can be greatly disrupted. The excessive sensory input overwhelms our cognitive capacity, and emotional system making it challenging to concentrate on tasks and filter out irrelevant stimuli. This compromised ability to sustain attention impairs our ability to engage in tasks and activities across different aspects of life.
What is Behavioral Regulation?
Behavioral regulation refers to the ability to manage and modulate our actions, responses, and behaviors in various situations. It involves self-control, impulse management, and the capacity to make thoughtful choices aligned with our goals and values. Behavioral regulation essentially is the ability to have agency and control over your actions. This also influences our ability to adapt to change and new environments and to maintain socially appropriate behavior in different social contexts.
How is Behavioral Regulation Related to Sensory Regulation?
Our ability to regulate and adapt our behaviors is deeply intertwined with sensory regulation. When we face challenges in sensory processing, such as feeling overwhelmed or highly sensitive to sensory input, it can have a significant impact on our behavioral regulation. These sensory difficulties can trigger stress responses which put us in fight-flight-freeze. Modifying our actions and behaviors becomes much more difficult when we are in a stress response state.
Sensory Regulation and Executive Functioning
Furthermore, sensory overload can also greatly impact our attention, focus, and executive functioning. The bombardment of sensory information can easily overwhelm our cognitive resources, making it difficult to concentrate on tasks or filter out irrelevant stimuli. Our ability to stay engaged and maintain sustained attention becomes compromised, affecting our productivity and performance in various areas of life.
What is Executive Functioning?
Executive functioning refers to a set of cognitive processes or skills that enable us to plan, organize, focus attention, regulate impulses, and achieve goals. It encompasses abilities such as working memory, flexible thinking, self-monitoring, and problem-solving. Executive functioning plays a critical role in goal-directed behavior, decision-making, and managing complex tasks.
How is Executive Functioning Related to Sensory Regulation?
Sensory regulation and executive functioning are closely intertwined, as sensory challenges can overload the brain. When the brain becomes overwhelmed, this significantly impacts executive functioning skills. By promoting sensory regulation, we are also supporting our executive functioning as it becomes easier to regulate our attention and focus.
Prioritizing Sensory Regulation: Establishing a Foundation for Effective Regulation
In this section, we explore the profound implications of prioritizing sensory regulation as the foundation for effective regulation. We examine why compliance-based systems and traditional therapy approaches often prioritize emotion regulation or behavior regulation without addressing sensory regulation fall short. Additionally, we will look at the importance of establishing a stable sensory foundation for successful regulation.
Building Stability Through Sensory Regulation
Compliance-based systems and many traditional therapeutic approaches tend to focus on addressing emotion regulation or behavior regulation without giving due attention to sensory regulation. However, overlooking the foundational role of sensory regulation can limit the effectiveness of these strategies. Just as trying to construct a house on wobbly ground leads to instability and constant setbacks, attempts to address emotions or behaviors without considering the dysregulation in the sensory system can yield limited results.
By acknowledging the crucial role of sensory regulation, we recognize the need to establish stability within the sensory domain as a first step. When the more foundational sensory regulation system is dysregulated, attempts to regulate emotions or behaviors become an upward battle!
To build a solid and enduring foundation for effective regulation, it is vital to address sensory dysregulation. We establish a stable base for emotional and behavioral regulation by providing support for sensory regulation through:
appropriate accommodations
sensory breaks
sensory-oriented interventions and therapies
Creating a sensory-friendly environment
we establish a stable base upon which emotion regulation and behavior regulation can more effectively take place. This comprehensive approach recognizes the interconnections between sensory, emotional, and behavioral regulation, paving the way for more successful outcomes.
A comprehensive approach to self-regulation will address the interconnections between sensory, emotional, and behavioral regulation, paving the way for successful self-regulation.
Implications for Teachers and Parents
Before addressing “bad” behavior, emotional outbursts, or inattention directly, ask yourself:
Is this person sensory-regulated?
How can I support and facilitate their sensory regulation?
How do I help this child get back to sensory safety?
Implications ADHD and Autistic Adults
When feeling irritable, angry, fatigued, or anxious. Do a sensory self-check-in:
Am I sensory dysregulated?
Is there something I can do to self-soothe until I get can get to sensory safety?
What is one action I can take to move toward sensory safety?
Implications Therapists and Caregivers
When you notice the person becoming stressed/anxious/agitated, consider these questions:
How can I reduce sensory input in the environment (dim lights, reduce noise, provide space)?
Are there sensory supports I can provide?
How can I reduce demands on this person until they can regain sensory safety?



Strategies for Sensory Regulation
Strategies for Neurodivergent Adults
Neurodivergent adults can benefit from various strategies to support sensory regulation and promote well-being. Here are some practical approaches that can be helpful:
Sensory Safety Plan: Develop a personalized sensory safety plan. By identifying activities or experiences that provide sensory input in a regulated and satisfying manner. This may include engaging in calming sensory activities, such as deep pressure touch, listening to soothing music, or incorporating sensory-friendly tools like fidget toys. This also includes creating a plan for managing sensory triggers and sensory-rich environments, including an exit strategy.
Environment Modification: Create a sensory-friendly environment by adjusting lighting, reducing noise levels, and considering the use of visual supports or organizational systems to enhance predictability and reduce sensory overload.
Mindfulness and Self-Care: Practice mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or guided meditation, to increase self-awareness and foster relaxation (remember, sensory overload puts our bodies in a stressed state, so learning relaxation strategies are a powerful tool in our sensory kit)! Prioritize self-care activities that promote sensory well-being, such as taking sensory breaks in quiet spaces or taking time to go pace out the extra energy.
Strategies for Parents and Teachers:
Parents and teachers can implement strategies to support children’s sensory regulation. Consider the following approaches:
Sensory-Friendly Classroom/Home Environment: Create a sensory-friendly environment by organizing spaces to minimize sensory distractions, providing visual schedules, and incorporating sensory tools like fidgets or sensory cushions, and providing alternative seating that allows children to move.
Sensory Breaks and Activities: Offer scheduled sensory breaks throughout the day to allow children to engage in activities that provide sensory input and promote regulation. Provide a range of sensory activities, such as sensory bins, calming corners, or movement breaks, to accommodate individual sensory needs.
Visual Supports and Routines: Utilize visual supports, such as visual schedules or social stories, to enhance predictability and help children understand expectations. Establish consistent routines that provide structure and support self-regulation.
Strategies for Caregivers and Therapists
Caregivers and therapists play a crucial role in supporting people with sensory regulation needs. Here are strategies that can be beneficial for caregivers:
Sensory Awareness: Develop an understanding of the sensory preferences and sensitivities of the individual in your care. Pay attention to their reactions to different sensory stimuli and make efforts to accommodate their needs.
Communication and Collaboration: Maintain open lines of communication and work collaboratively to develop strategies that promote sensory regulation. Encourage them to explore their sensory experiences and preferences in safe environments.
Sensory Breaks: Offer opportunities for sensory breaks, providing a calm and quiet space where the individual can engage in sensory activities or take time for self-regulation. Respect their need for breaks when a sensory overload occurs.
 Sensory Regulation 101: Sensory Safety Plan (Personal Use)
Sensory Regulation 101: Sensory Safety Plan (Personal Use)
By implementing these strategies, neurodivergent adults, caregivers, therapists, parents, and teachers can create a supportive and inclusive environment that fosters sensory regulation and well-being. Remember to tailor the approaches to individual needs, collaborating and communicating openly.
Conclusion
The interplay between sensory regulation and emotional well-being holds significant implications for neurodivergent people. Sensory dysregulation can profoundly impact emotional experiences, intensifying sensitivity or leading to shutdown. By prioritizing sensory regulation, integrating and adjusting sensory input, managing arousal levels, attention, and emotional responses, we foster an environment that enhances emotional resilience and regulation skills, promoting overall well-being in our emotional worlds.
Embracing the importance of sensory safety unlocks the power of self-regulation. Sensory regulation forms the backbone of navigating the world with greater ease and well-being. Whether you’re neurodivergent or a caregiver, implementing sensory regulation strategies fosters a supportive environment and empowers self-regulation skills. Embrace the journey of self-regulation, guided by sensory safety principles, and thrive in our diverse world.